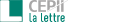This Working Paper builds a novel dataset of sector-level energy prices to reassess the role of energy costs in industrial performance after the post-COVID recovery and the war in Ukraine. The authors argue that focusing solely on energy prices my overlook the crucial influence of domestic demand, which is heavily shaped by fiscal policy. Expansionary fiscal measures can stimulate short-run industrial output by boosting domestic sales. Competitiveness gains from lower energy prices can be offset by demand-boosting fiscal policy, while contractionary policies can partly soften the impact of higher energy costs. Carl Grekou, Thomas Grjebine, Florian Morvillier
>>> |
How does the electoral success of a far-right political force shape the strategies and policy platforms of mainstream candidates? This Working Paper exploits the political shock of the creation of the Front National, an anti-immigration party, in 1972 and its sudden electoral breakthrough in the 1980s. Through a comprehensive textual analysis of candidate manifestos in French parliamentary elections from 1968 to 1997, the authors find that right-wing candidates respond to local far-right success, measured as voting shares, by amplifying the salience of immigration in their manifestos. They also adopt more negative positions on immigration and increasingly associate it with issues such as crime and the welfare state. In contrast, the ideological positions of left-wing candidates do not shift in response to far-right electoral gains. The Papers shows that the strategic adjustments of right-wing candidates help mitigate electoral losses to far-right competitors. Anthony Edo, Thomas Renault, Jérôme Valette
>>> |
This Working Paper shows that US monetary tightening generates global spillovers through the remittance channel, with outflows falling in source countries and amplifying the global financial cycle. The author uncovers an inverse U-shaped relationship between remittance dependence and output responses: moderate inflows buffer shocks, while high dependence (above 4% of GDP) magnifies recessionary effects. The Paper documents strong heterogeneity driven by migrant skill composition: low-skilled diasporas generate pro-cyclical remittances and higher vulnerability, whereas skilled or diversified diasporas stabilize remittance flows. Pablo Aguilar-Perez
>>> |
- Low-Value Packages: An Illustration of China’s Export Reorientation Toward the EU
Charlotte Emlinger, Kevin Lefebvre, Vincent Vicard - Immigrant Employment in Intermediate Sectors Enhances Downstream Export Performance
Amandine Aubry, Anthony Edo
- The Impact of the Far Right on Mainstream Politics: Evidence from the Front National
Anthony Edo, Thomas Renault, Jérôme Valette - Energy and Fiscal Shocks: Reassessing Industrial Competitiveness
Carl Grekou, Thomas Grjebine, Florian Morvillier - Immigration, Identity Choices, and Cultural Diversity
Yasmine Elkhateeb, Riccardo Turati, Jérôme Valette - Sectoral Linkages and the Impact of Immigration on Export Performance
Amandine Aubry, Anthony Edo - Labor Market Power, Export Prices and Pass-through
Malik Curuk, Jérôme Héricourt, Gonzague Vannoorenberghe - International Trade by Production Stage: What’s Real?
Pierre Cotterlaz, Guillaume Gaulier, Aude Sztulman, Deniz Ünal - Do Anti-immigration Attitudes Discourage Immigration? Evidence from a New Instrument
Etienne Bacher, Michel Beine, Hillel Rapoport - Monetary Policy and Life Insurance Profitability: Bancassurance’s Edge in a Low-Yield World
Pablo Aguilar-Perez - Global Spillovers of US Monetary Policy: New Insights from the Remittance Channel
Pablo Aguilar-Perez
- Labour Economics
Does Immigration Affect Native Wages? A Meta-Analysis
Amandine Aubry, Jérôme Héricourt, Léa Marchal, Clément Nedoncelle
Spending Smarter: How Efficient and Well-Allocated Public Spending Can Boost Economic Growth
Download the presentations
7th EMME Workshop Emerging Market MacroEconomics
March 20, 2026
Low-Value Packages: An Illustration of China’s Export Reorientation Toward the EU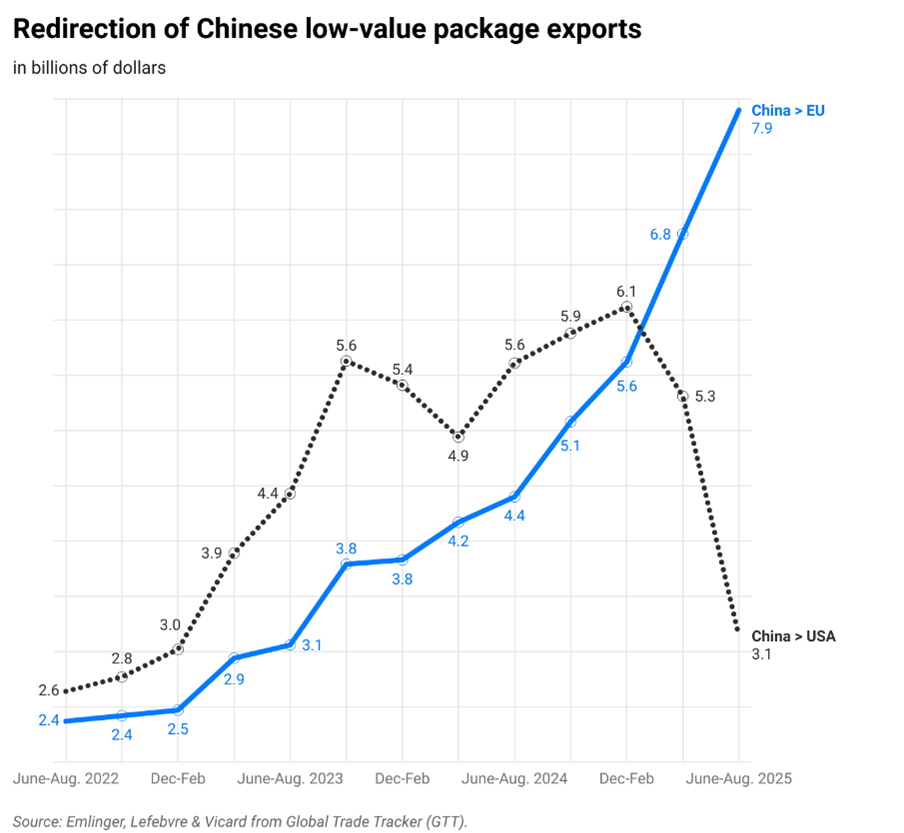 In response to the sharp increase in U.S. tariffs on Chinese imports, Beijing is redirecting part of its export flows toward new markets. For certain products, the European Union has emerged as a preferred destination. Charlotte Emlinger, Kevin Lefebvre, Vincent Vicard >>> |
Immigrant Employment in Intermediate Sectors Enhances Downstream Export Performance
A sector’s export performance depends not only on the immigrant labour it employs directly, but also on immigrant workers employed in upstream sectors. Amandine Aubry, Anthony Edo
>>> |
.jpg) We were glad to host a discussion on the latest FMI Fiscal Monitor with Danila Smirnov (IMF) and Jérôme Héricourt (CEPII and University Evry Paris-Saclay). Global public debt is on an increasingly worrying path. It is projected to rise above 100% of global GDP by 2029, which would be the highest level since 1948. Under adverse scenarios, it could reach 124%. Although major economies typically have access to the capital markets to finance and refinance their substantial debt, many emerging and low-income countries face severe fiscal risks, even with lower debt ratios, due to limited financing options and low debt tolerance. Meanwhile, higher interest rates, stretched financial valuations and mounting spending pressures - from defence to climate-related disasters - are exacerbating vulnerabilities. This conference explored the essential reforms needed to strengthen growth, efficiency and public trust, to restore debt sustainability, and to reduce the risk of fiscal-financial feedback loops. The presentations are available for download. >>> |
- Contact us
- Our other sites
 |
ISSN: 1255-7072
Editorial Director : Antoine BouëtManaging Editor : Evgenia Korotkova






.jpg)